Most of students search over Google for Haryana Board (HBSE) Important Questions 2026. Here is the Main reason because HBSE Board Says that in HBSE Exam 2026 (last 3 Years of Questions will Repeat) so that here are the selected List of Questions of Haryana Board For Class 12.
HBSE Class 12 Physical Education Important Question Answer 2026
Chapter 1 – Planning in Sports
Q1. What are the Objectives of Management? Most Important
Ans –
- Goal oriented: Planning is a goal-oriented activity, i.e., it gives direction and vision to the conducting of sports events. Without determining the goal, a plan cannot be executed. Planning aims at realistic goal settings and their attainment.
- Policy: Development of a policy is very important to set boundaries for overall conduct of the event. This will serve as a guide and assist in decision making.
- Economy: Planning helps in cost reduction, as it increases coordination and financial control. Budget should be prepared in quantitative terms, covering all aspects of the sports events which are to be conducted.
- Rules and regulations: Guidelines comprising rules and regulations of games or tournament should be prepared and published well in advance to keep the scope for subjectivity and bias in judgement very low.
- Strategy: It provides the way through which an organisation can successfully achieve its goals, i.e., successfully conduct the event.
Q2. Differentiate between knockout and league tournament. Most Important
OR
What is Knock-out Tournament?
OR
What is League tournament?
Ans – Knockout Tournament : In a Knock-Out Tournament a player or team continues to play matches until it is defeated. In this type of format, players or teams have to consistently give their best performance to avoid elimination
League or Round Robin Tournament : In League or Round Robin Tournament, a player or team will play the matches that are allotted before the start of the tournament. Fixed number of matches are given to players and teams, and losing one or all can put them out of the tournament. Players or teams will get equal chance to play with each other. Thus, the true winner emerges from this format and ranking can be prepared for all participating players or teams.
Q3. What is meant by a league or Round-Robin tournament? Describe its advantages and disadvantages.
Ans – A League Tournament (also called a Round-Robin Tournament) is a type of competition in which each team plays with every other team, regardless of win or loss. The team that earns the maximum points at the end of all matches is declared the winner.
Advantages of League or Round-Robin Tournament
- True Champion is Decided: Every team plays against all others, so the best and most consistent team wins.
- More Opportunities for Players: Each team gets to play several matches, which improves skill and experience.
- Good Publicity and Spectator Interest: More matches mean more entertainment and audience engagement.
- Less Chance of Elimination by Luck: Unlike knock-out tournaments, one bad match does not eliminate a team.
- Better Team Assessment: Helps in ranking teams accurately for future competitions.
Disadvantages of League or Round-Robin Tournament
- Time-Consuming: Large number of matches makes it lengthy to complete.
- Expensive: Requires more funds for travel, accommodation, and arrangements.
- Fatigue and Injuries: Continuous matches cause tiredness and increase injury risk.
- Difficult to Manage: Needs proper scheduling, venues, and officials for many matches.
- Less Excitement in Later Stages: When winners are already clear, remaining matches may not attract interest.
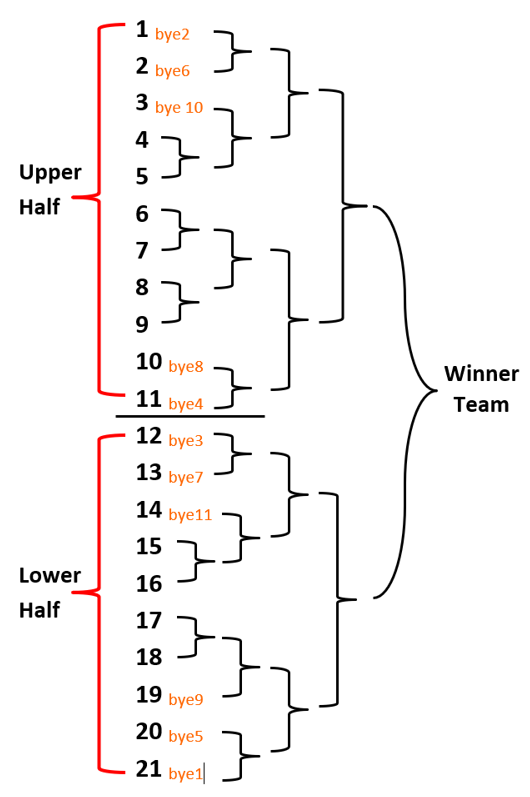
Q4. Draw the Fixture of 21 Teams in Knockout Tournament. Most Important
Ans – Total Number of teams = 21
Number to byes will be given according to 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 Concept. So, Total Number of byes – 32 – 21 = 11
Total Number of byes in Upper Half = $latex \displaystyle \frac{{\text{(N -1)}}}{2}$
Total Number of byes in Lower Half = $latex \displaystyle \frac{{\text{(N +1)}}}{2}$
Total Number of Matches – (N -1) = 21 – 1 = 20 Matches
Teams in Upper Half = $latex \displaystyle \frac{{\text{(N +1)}}}{2}$ = 11 Teams
Teams in lower Half = = 10 Teams
Fixture of 21 Teams –
Q5. Define Intramural Tournament and Write the objectives of Intramural Tournament. Most Important
OR
What is main objective of Intramural activities?
Ans – The meaning of the word ‘intramural’ is “within the walls”. In context of sports, it refers to a tournament conducted within the walls of a single institution/ school/ community. Intramural competitions/tournament are conducted within players of one institution.
Objectives of Intramural Tournament are following –
- To encourage mass participation in sports in an institution.
- To focus on all-round development of children.
- To focus on fitness, wellness and health aspects of children.
- To promote curricular integration through sports.
- To help children to develop personality
Chapter 2 – Sports & Nutrition
Q1. Differentiate between Macro and Micro Nutrients.
Ans –
| Macro Nutrients | Micro Nutrients |
|
|
Q2. Explain different types of nutrients and their function and sources. Most Important
Ans – There are different type of nutrients as following –
- Carbohydrate
- Protein
- Fat
- Vitamin
- Dietary Fibre or Roughage
Sources of Nutrients are as follows –
Carbohydrate – Carbohydrates provide energy needed by the body and the nervous system, brain and red blood cells. Some sources of carbohydrates are Fruits, cereal grains, milk, suger, rice, vegetables, pasta, breads etc.
Protein – Proteins build & repair body cells and a form part of various enzymes, hormones, and antibodies. Protein also provide energy to body. Some sources of protein are Milk and milk products, grains, fish, eggs, poultry, meat etc.
Fat – Fats provide energy, Carry vitamins and help in regulation of hormones. some sources of fat are meat, poultry, fish, milk and milk products, nuts and seeds, vegetable oils, desi ghee, vanaspati ghee, butter, margarine, cheese
Vitamin – vitamins help in regulation of body hormones and digest of macronutrients. some sources of vitamin are milk, cheese, cream, butter, egg yolk, liver, carrots, pumpkin, mangoes, papaya, soybean, corn, cottonseed, safflower, green leafy vegetables etc.
Dietary Fibre or Roughage – Dietary fibre or roughage provides feeling of fullness, helps in smooth elimination of stool, prevents diseases like cancer, diabetes and heart disease, has cholesterol lowering effect. Some sources of Roughage are wheat atta, whole pulses, peas, beans, vegetables, fruits like guava, orange, pineapple etc.
Q3. Write down some sources of Vitamin A.
Ans – milk, cheese, cream, butter, egg yolk, liver, dark green leafy vegetables; red and yellow fruits and vegetables (carrots, pumpkin, mangoes, papaya).
Q4. Write down some sources of Vitamin D.
Ans – Egg yolks, liver, fatty fish, fortified foods. When exposed to sunlight, the skin can make vitamin D.
Q5. Write down some sources of Vitamin E.
Ans – soybean, corn, cottonseed, safflower, green leafy vegetables, wheat germ, wholegrain products, nuts and seeds.
Q6. Write down some sources of Vitamin K.
Ans – green leafy vegetables, cabbage and Milk.
Q7. Write down some sources of Calcium.
Ans – Milk and milk products, fish with bones (eg., sardines), fortified soya milk, greens (broccoli, mustard leaves), pulses
Q8. What do you understand by a balanced diet? Most Important
Ans – Balanced Diet is eating a wide variety of foods in the right proportions, and consuming the right amount of food and drink to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight.
Q9. What is BMI? Write the formula for calculating BMI. Most Important
Ans – Body Mass Index (BMI) is used to broadly categorize a person as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese based on tissue mass (muscle, fat, and bone) and height.
Formula for calculate BMI is $latex \displaystyle \frac{{\text{Weight (Kg)}}}{{\text{Heigh}{{\text{t}}^{\text{2}}}\text{(m)}}}$
Q10. Name the different types of vitamins. From which substances are they obtained?
Ans – Vitamins are mainly of two types — Fat-soluble vitamins and Water-soluble vitamins.
Fat-soluble vitamins:
- These dissolve in fat and are stored in the body’s fatty tissues and liver.
- Vitamins: A, D, E, and K
- Sources: Milk, butter, fish oil, eggs, leafy vegetables, sunlight, and nuts.
Water-soluble vitamins:
- These dissolve in water and are not stored in the body, so they must be taken daily through food.
- Vitamins: B-complex (B₁, B₂, B₃, B₆, B₁₂, etc.) and Vitamin C
- Sources: Fruits, green vegetables, whole grains, pulses, and citrus fruits like orange and lemon.
Chapter 3 – Yoga & Lifestyle
Q1. Discuss Asanas as a preventive measure for disease.
OR
“Asanas can be used as a preventive measures.” Comment
OR
Write down in brief about Yoga. Most Important
Ans – Yoga plays an important role in helping individuals adopt a healthier lifestyle for improved physical and mental health, which, in turn, results in better productivity. Yoga is therapeutic in modern lifestyle disease like stress, diabetes, hypertension, backache etc. The power of yoga lies in its simplicity, flexibility, and diversity. As a result, Yoga has been the subject of global popularity and research in the past few decades.
Q2. Explain Diabetes and its symptoms. Most Important
Ans – Diabetes is a metabolic disorder where there is a defect in utilization of sugar by the body.
Symptoms
• Excessive urination.
• Excessive thirst.
• Dehydration due to excessive urinary output.
• Increased appetite.
• Loss of body weight
• decreased resistance
Q3. Explain Asthma and its symptoms. Most Important
Ans – Asthma is a disease of the respiratory system where the airways get narrowed, often in response to a “trigger” such as exposure to an allergen, cold air, exercise, or emotional stress.
Symptoms –
- Asthma is characterized by episodic dyspnea (difficulty in breathing), wheezing and cough.
- There is difficulty in expiration.
- Patient may experience tightness of the chest/discomfort in the chest.
- The attack may last from one to several hours.
- Severe attack, called “status asthmaticus”, is often not responsive to usual therapy. It is a medical emergency and may affect the heart and circulatory system.
- Hypercapnia (increased level of CO2), acidosis and hypoxia (decreased O2 level), may occur in Asthma, though these conditions are rare.
Q4. Discuss the asanas helpful for a person suffering from asthma. Most Important
Ans – Gomukhasana, Chakrasana, Parvatasna, Bhujanasana, Sukhasana, Matsyasana, Paschimottanasana
Q5. Write down the benefits and contraindications of Savasana in detail. Most Important
Ans –
Benefits
• It helps reduce stress and removes physical and mental fatigue.
• It relaxes all muscles and nerves of the body
• It is helpful to overcome psychological disorders.
• It is very beneficial for managing high blood pressure, cardiac diseases and anxiety disorders.
Contraindications
• A very distracted mind is going to find it difficult to relax and by pushing the body, it will cause more irritation and bring a headache.
• Someone with severe acidity may find lying on the back very uncomfortable as the food pipe may cause irritation.
Q6. Explain the procedure and benefits of any one asana for back pain.
OR
Explain Parvatasana Procedure and Benefits.
Ans – There are many asana for relief in back pain. Parvatasana is easy to do and effective asana among them.
Procedure :
1. Sit straight on yoga mat in the lotus position with both hands resting on knees palms down.
2. Raise your hands to the front and clasp together with palms outwards.
3. Lift your hands over your head straight with palms facing up.
4. Stretch and hold the position for few seconds. Repeat multiple times.
5. Stand straight on your yoga mat with legs together and hands to the sides.
6. Lift your hands up and bring them down. As you do this, bend from the waist.
7. Reach to the floor at an angle.
8. Let your legs be straight and firm on the floor. Make sure you do not bend knees.
9. Keep the shape of exactly 45° relative to floor.
10. Keep this position for few seconds and release.
11. Repeat multiple times.
Benefits
1. If done in the morning, Parvatasana keeps you alert.
2. Parvatasana stretches the spine. The stretch in this pose reduces extra fat in the back and waist.
3. It helps practitioners below 18 years to gain some height.
4. It is helpful in ameliorating respiratory disorders including asthma.
5. It helps to reduce back pain.
Chapter 4 – Physical Education & Sports for CWSN
Q1. Write in detail about Disability.
OR
Define disability and list down any two types of disability.
Ans – Disability is understood as a condition that produces a long-term impairment that affects activities of daily living, such as eating, walking, and maintaining personal hygiene. Disability may be
• congenital, or present from birth,
• occurring during a person’s life time,
• invisible disability (not noticeable easily) and
• temporary disability (recovery is possible).
Q2. What is the role of positive and energetic attitude in dealing with person with Disability?
OR
How can you make a person with disability feel comfortable?
Ans – One should approach a person with special needs with positive energy and attitude. Approach should be warm and friendly. One should not show sympathy for, or, even in certain cases, fear of the person.
Q3. Create a mind map including any six advantages of physical activities for children with special needs.
OR
“Participation in physical activities is advantageous for children with special need.” Briefly explain any six advantages. Most Important
OR
How are physical activities helpful for children with special needs?
OR
Write any two advantages of physical activities for Children With Special Needs (CWSN).
Ans – There are the following advantages of Physical activities for CWSN :
• Physical benefits – Children with intellectual disabilities may have additional physical disabilities resulting in below age-level performance in typical motor skills. Regular involvement in physical education and sport can help them to develop their gross motor and fine motor skills which may improve their overall performance.
• Mode of Recreation and Fun – CWSN frequently miss out on social activities, recreation and fun. Participation in extracurricular and sports activities can help them overcome this obstacle, providing them with the ability to engage in social interactions, make friends and initiate social skills.
• Improved Emotional Health – Including physical activity in a healthy lifestyle is proven to decrease rates of depression. CWSN often tend to have more emotional problems like depression. Participating in regular exercise can be a life-changing benefit by improving mental health and wellbeing.
• Channelizing the Surplus Energy – Children with disabilities like ADHD display hyperactivity that, if appropriately directed, can bear positive results regarding cognitive benefits and constructive behaviour.
• Psychological benefits – Physical activity improves general mood and wellness in CWSN by improving their self-esteem, social awareness, and self- confidence, all of which are factors essential for empowering their lives.
• Healthy lifestyle – CWSN are about twice as likely as other children to be overweight or obese often due to the related greater likelihood of being sedentary. As a result of their disability, their levels of participation in sports and physical activity is much lower than their peers. Physical activities improves their health and improve lifestyle.
Chapter 5 – Children & Women in Sports
Q1. Define Motor Development. Most Important
Ans – motor development refers to the development of a child’s bones, muscles and ability to move around and manipulate her or his environment.
Q2. What is meant by Round Shoulders? Mention a few exercises to correct it.
OR
What do you understand by Round shoulders deformity? Suggest any four corrective measures for round shoulders.
Ans – Round shoulders is a postural deformity in which shoulders are bent forward from the ideal alignment, thereby giving a narrow curve to upper back. It leads to postural deviations such as hyperkyphosis, or hunch back and anterior head carriage, or forward head posture.
Corrective Measures for Round Shoulders –
Corrective measures for rounded shoulders is strengthening and stretching of muscles and trying to correct the imbalance of muscles by doing chest stretches, T stretch, wall stretch, Handclasp stretch and planks, pull ups, reverse shoulder stretch, etc. Yoga asanas like Chakrasana, Dhanurasana, can be useful in correcting rounded shoulders.
Q3. What is meant by Scoliosis?
OR
Explain Scoliosis Deformity. Most Important
Ans – Scoliosis is a position in which the spine is tilted to either side of the body. It is a position of exaggerated lateral curvature or sideways curvature of the spine. In this disorder, the spine bends, twists or rotates in a way that it makes a C or an S shape.
Q4. Explain the various constraints faced by women in sports. Most Important
Ans – There are the following constraints faced by women in sports –
1. Physical Constraints – Physical constraints refer to the qualities of the sports person such as the physical fitness parameters. If there is failure in any of these required parameters it results in the reduction of sports performance.
2. Physiological Constraints – If there is any dysfunction of the organs it results in reduction of sports performance. Some women have lower levels of RBCs, lower percentage of Haemoglobin, smaller or weaker heart and it circulation, smaller or weaker lungs and breathing mechanism, dysfunction of organs of endocrine system, greater body fat percentage, dominance of neither aerobic power nor anaerobic power, Menstrual disorders.
3. Psychological Constraints – Psychological constraints comprise the behavioural process such as higher level of anxiety or aggression, lack of self- confidence, achievement motivation or interest, lower self-esteem or hesitation to participate during menstrual periods.
4. Social Constraints – Social constraints refer to the behaviour of society in general and sports field in particular. During training and competition, the relationship with coaches, arena persons, training-mates, co-participants, opponents and officials during competition affects not just performance, but also participation. If there is any undue harassment or misbehaviour during this period, it results in reduction in sports performance or ultimately exit from sports participation. Lack of parental support and encouragement, and male dominant social structure also has a very negative impact on participation.
5. Religious Constraints – Religious constraints prevail in those societies who are fundamentalist and have rigid religious beliefs. They fear as society may ostracise them for going beyond the boundaries of their religion. This might also be the cause of limited participation in sports by women in India.
Chapter 6 – Test & Measurement in Sports
Q1. What is Vo2 Max?
OR
What is Aerobic Capacity?
Ans – The maximum rate of oxygen used by heart, lungs and muscles during the exercise. It also known to measure aerobic capacity of an individual.
Chapter 7 – Physiology & Injuries in Sports
Q1. Elucidate any six effects of exercise on muscular system. Most Important
OR
Explain the effect of exercise on Muscular System.
Ans –
1. Increased blood supply: During exercise, in order to match demand of fuel to muscle, the supply or concentration of blood increases in the whole body.
2. Increased muscle temperature: During exercises muscles demand energy, which comes from contracting muscles. During the process, a lot of heat energy is generated which increases the temperature of muscles.
3. Increased muscle flexibility: Due to increase in blood flow and rise in temperature, elasticity of muscles increases.
4. Accumulation of Lactate: Muscles requires oxygen. If blood supply does not provide appropriate volume of oxygen to muscles, it leads to accumulation of lactate acid in muscles which result in pain, and soreness in muscles.
5. Micro-tears in Muscle Fibres: During exercises muscle tissue is placed under stress which results in micro-tears in muscle fibres. The body responds by repairing the muscle fibres and making them larger.
6. Hypertrophy of Muscle: Scientific and systematic exercise leads to increase in thickness of muscle fibres that results in increase in muscle size
Q2. What is a strain? Write its cause, prevention and treatment. Most Important
Ans – A strain is an injury to either a muscle or a tendon generally caused by overuse, force, or stretching. Depending on the severity of the injury, a strain may be a simple overstretch of the muscle or tendon, or it can result in a partial or complete tear. A strain could be an acute or chronic soft tissue injury that is a twist, pull or tear of a muscle or the tendon.
Cause – Strains occur suddenly (acute strain) or develop slowly over time (chronic strain). CauseIt includes lifting of heavy objects, running, jumping, throwing etc.
Prevention – Regular stretching and strengthening exercise for any kind of sport can be the preventive measure for strain.
Treatment – It can be managed by applying ice packs and maintaining the strained muscle in a stretched position. (RICE: rest, ice, compression and elevation).
Q3. What is a sprain? Write its cause, prevention and treatment. Most Important
OR
What is Sprain?
OR
What is a Sprain? Describe its causes, symptoms and treatment.
Ans – A sprain is an injury to a ligament (the tough tissue that connects bones at a joint) caused by overstretching or tearing due to sudden twist or force. It usually occurs in joints like the ankle, knee, or wrist.
Causes of Sprain
• Sudden twisting or turning of a joint during movement.
• Falling or slipping awkwardly.
• Uneven playing surface or wrong landing after a jump.
• Weak ligaments due to fatigue or lack of warm-up.
• Improper footwear or poor posture while exercising.
Symptoms of Sprain
• Severe pain at the injured joint.
• Swelling and tenderness around the area.
• Bruising or discoloration of the skin.
• Restricted movement of the joint.
• In severe cases, the joint may feel unstable or loose.
Treatment of Sprain
First-Aid and Medical Care follow the R.I.C.E. Principle:
R – Rest: Stop all movement; do not put weight on the affected joint.
I – Ice: Apply an ice pack for 15–20 minutes every 2–3 hours to reduce swelling and pain.
C – Compression: Use an elastic bandage to compress and support the joint.
E – Elevation: Keep the injured part raised above heart level to reduce swelling.
Q4. What is Fracture? Name the more common types of fractures and describe them. Most Important
OR
Define Fracture and explain any four types of fracture.
OR
Elucidate any four types of fractures.
Ans – A fracture is a break in a bone. Fractures are caused by a direct impact, such as a fall or a severe tackle. Stress fractures develop over time and are caused by overuse.
Type of Fractures –
Stress Fracture – Stress fractures may occur because of overuse injuries and the failure to have adequate equipment to protect the body.
Greenstick – A fracture in a young, soft bone, in which the bone bends. These fractures most commonly occur with a fall.
Comminuted – A fracture in which a bone is broken, splinted or crushed into number of pieces.
Transverse – Transverse fracture is when there is a straight break right across a bone.
Oblique – Oblique fracture is one in which the bone breaks diagonally.
Impacted – This type of fracture occurs when the broken ends of the bones are jammed together by the force of the injury.
Q5. Define First Aid. Most Important
Ans – First Aid refers to the treatment which is given to the casualty suffering from either a minor or serious illness or injury, to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening, or to promote recovery.
Q6. Write down the aims and objectives of first aid.
OR
Describe any 2 objectives of first aid.
Ans – The basic aim and objectives of First Aid are –
• To prepare properly for any emergent situation to avoid errors and act quickly and calmly.
• To assess and care life-threatening conditions first
• To minimize further injury, infection and complications
• To make the victims comfortable as possible which enable him to save energy.
• To transport the victim to a medical facility as per necessity.
Q7. Explain P.R.I.C.E in Detail. Most Important
Ans – P.R.I.C.E. stand form Protection, Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation.
Protection
Protect the affected area from further injury by limiting or avoiding weight-bearing through the use of crutches, a cane, or hiking poles. Partially immobilizing the injured area by using a sling, splint, or brace may also be a means of protection.
Rest
• Stop using injured part or discontinue activity. It could cause further injury, delay healing, increase pain and stimulate bleeding.
• Use crutches to avoid bearing weight on injuries of the leg, knee, ankle and foot.
• Use splint for injuries of the arm, elbow, wrist and hand.
Ice
• Ice application contracts blood vessels.
• Helps stop internal bleeding from injured capillaries and blood vessels.
• Hastens healing time by reducing swelling around injury.
• Keep damp or dry cloth between skin and ice pack.
• Do not apply ice for longer than 15 to 20 minutes at a time.
• Apply every hour for 10 to 20 minutes.
• Apply ice as long as pain or inflammation persists.
Compression
• Hastens healing time by reducing swelling around injury.
• Decreases seeping of fluid into injured area from adjacent tissues.
• Use elasticised bandage, compression sleeve, or cloth.
• Wrap injured part firmly.
• Do not impair blood supply.
• Too tight bandage may cause more swelling.
• Wrap over ice.
• Loosen the bandage if it gets too tight.
Elevation
• Elevate injured part above the level of heart.
• Decreases swelling and pain.
• Use objects and pillows.
Q8. Point out physiological factor for strength.
OR
Explain any three physiological factors determining strength.
Ans –
1. Muscle cross-sectional area: It is generally measured with girth measurement. The muscle having bigger cross-section area has more strength because larger muscles have better quality of action and myosin filaments.
2. Types of muscle fibre: There are two basic types of fibres. (i) Slow twitch fibres (ii) Fast twitch fibres. Fast twitch muscle fibres lead to increase in muscle size and strength with greater explosive power. Every individual has different ratios of slow and fast twitch muscle fibres.
3. Muscle length: Persons with relatively long muscles have greater potential for developing size and strength than person with relatively short muscles.
4. Age and gender: Muscle strength declines with age due to decrease in muscle cross-sectional area. The strength changes with increase in age specially after 15 years. Men and women have similar tissues but men have bigger muscle size leading to better strength as compared to women.
Q9. Explain any 2 physiological factors, help in determining endurance.
OR
Briefly explain any two factors determining endurance.
Ans –
1. Aerobic capacity : To perform an activity continuously energy is required by the muscles which can be supplied in the presence of oxygen. Therefore the ability or organism to maintain the adequate supply to oxygen to the working muscles for energy liberation is important for endurance performance.
2. Anaerobic capacity : The working capacity of muscle in absence of oxygen is called anaerobic capacity. more or less Anaerobic capacity is required in all kind of endurance activities.
Chapter 8 – Biomechanics & Sports
Q1. List Newton’s Laws of Motion. Most Important
Ans – Sir Issac Newton gave three laws of motion. which are given below –
Newton’s First Law of Motion: Law of Inertia
Newton’s Second Law of Motion: Law of Acceleration or Law of Resultant Force
Newton’s Third Law of Motion: Law of Reaction or Law of Reciprocal Action Force
Q2. Define Friction. Most Important
Ans – Force acting over the area of contact between two surfaces in the direction opposite that of motion or motion tendency is called friction.
Q3. Discuss various types of friction.
OR
Mention any two types of friction by giving suitable examples from sports.
Ans – In the field of sports, we will study following types of friction.
1. Static friction: Static friction is friction that exists before an object starts to slide. For example, When you hit a cricket ball with a bat, or a tennis ball with racket, or in rock climbing where hand and feet are static.
2. Kinetic or Sliding friction: Kinetic friction is friction that is created when the object starts to slide. For example, when an ice skater is skating, or friction produced while rubbing hands.
3. Rolling friction: Rolling friction is friction when an object rolls on the surface. For example, a ball bearing, any ball rolling on the ground.
4. Fluid Friction (Air and Water resistance): Fluid friction is friction when the movement of an object or a person is hindered or meets resistance from water or air. For example, swimming, diving, sky diving, discuss and javelin floating in air, high jump etc.
Chapter 9 – Psychology & Sports
Q1. Differentiate between Introvert and Extrovert personality?
Ans –
Introvert Extrovert
• Interested in their own self
• Reserved
• Self-aware and introspective
• Take pleasure in reading, writing
• Tend to shy away from public
• Think before acting • Highly socialized
• Broad-minded
• Expressive and enjoy centre of attention
• Meet unknown people easily
• Bold, outgoing and optimistic person
• Action oriented
Q2. Differentiate between Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation.
Ans –
Intrinsic Motivation Extrinsic Motivation
• Driving force to pursue an action for fun, joy or any other inner satisfaction
• Internal factors like joy, enjoyment
• Goal Setting strategies, Family and Community support
• Long term benefit of maintaining a behaviour • Driving force to pursue an action due to reward, trophy, money, promotions or praise
• External factors like reward, promotion, praise
• Associating success with future benefits, awards, promotions and avenues.
• Helpful to initiate or create a drive towards a desired behaviour when internal factors are missing.
Q3. Define aggression. Discuss any 2 types of aggression. Most Important
Ans – Aggression is behaviour that is hostile and violates other people’s rights.
1. Hostile aggression or reactive aggression – Hostile aggression is a type of aggression that is committed in response to a perceived threat or insult. It is unplanned, reactionary, impulsive, and fuelled by intense emotion as opposed to desire to achieve a goal. Aggressors typically have a sense of a loss of control during outbursts, and characteristically experience physiological hyperarousal. Thus, it is also sometimes known as reactive aggression.
2. Instrumental aggression – instrumental aggression refers to aggressive behaviour meant or used to attain some non-aggressive goals like winning, getting money, prestige or gaining any other advantage. Instrumental aggression is harmful behaviour engaged in without provocation to obtain an outcome or coerce others.
Q4. What is the full form of SMART?
Ans – SMART – Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, Time based
Q5. Write short note on Goal setting.
OR
What do you understand by “Goal Setting”?
Ans – Goal setting is a mental training technique that can be used to increase an individual’s commitment towards achieving a specific standard of proficiency on a task within a specified time. It is a process of establishing a level of performance proficiency which should be reached within a prescribed time period is known as goal setting.
Chapter 10 – Training in Sports
Q1. Explain Isokinetic exercise with suitable examples. Most Important
OR
What are Isokinetic Exercises?
Ans – In isokinetic contraction, the muscles apply maximal force throughout the range of motion around the joint. This method of exercise was introduced by J.J. Perrine in 1968 and involves special type of muscle contraction called isokinetic contraction generally used in sporting events like rowing and swimming. These exercises are performed on specially designed instruments.
Q2. Write about the different types of Endurance based on duration of activity. Most Important
Ans – There are following four type of endurance based on duration of activity.
Speed Endurance: Speed Endurance is the ability to resist fatigue in cyclic activities that last up to 45 seconds. Eg. 400m Sprint
Short Term Endurance: Short Term Endurance is needed for the activities that last from 45 seconds to about 2 minutes. Eg. 800m run.
Medium Time Endurance: To resist fatigue in activities that lasting from 2 minutes to about 11 minutes medium time endurance is used. Eg. 1500m, 3000m, etc.
Long Time Endurance: Long Time Endurance is needed for the activities that last for more than 11 minutes. Eg. Marathons, cross country races etc.
Q3. What do you mean by endurance? Explain methods to develop endurance in detail. Most Important
OR
Define Endurance and discuss the methods of endurance development.
OR
What is Fartlek Training?
Ans – Endurance is, thus, the ability of an individual to sustain an activity for a long period without undue fatigue. Like strength, endurance is also a conditional ability. Endurance has been studied thoroughly and deeply because it holds great importance in health, training and competition.
There are following three type of training method which develop endurance.
Continuous Method : this method is about continuity. In this method, an exercise is done for a long duration of time without any rest. Because the duration of the activity is long and continuous in nature, the intensity of the activity is set to be low.
Interval Method : This is the most versatile method used for improving endurance. In this method, the activity is done at a comparatively high intensity with intervals or breaks of incomplete recovery.
Fartlek Method : Fartlek is a Swedish word which means ‘speed play’. in the Fartlek method the speed variation is not planned. The athlete changes the speed with his own accord during the activity due to the changes in terrain, surroundings and his feelings.
Q4. Write various methods to develop speed. Most Important
OR
Briefly describe the methods of development of speed.
Ans –
Acceleration Runs: This method is generally used to develop speed while attaining maximum speed from a static position. In acceleration run, a sportsperson is required to run a specific distance. After the start, the athlete tries to gain maximum speed at the earliest and finishes the specified distance at that speed. These runs are repeated with sufficient rest between the runs. It usually takes 50-60 meters for a sprinter to attain maximum speed after the start.
Pace Runs: Unlike acceleration runs, pace runs incorporate the method of running the set distance at a uniform speed. It usually includes races of 800 meters and above.
Q5. Define flexibility. What is active and passive flexibility? Explain any two methods used to develop flexibility.
OR
Define Flexibility and list down its types.
Ans – Flexibility is also known as range of motion around a joint. It is the ability to execute a movement with greater amplitude or range. Flexibility is about 2 types which are following :
Type of Flexibility :
1. Active Flexibility :The ability to perform a movement with greater amplitude without an external help is called active flexibility. It is the range of motion that you can achieve by using your muscles to put your joint there, eg., using your shoulder muscles to pull your arm back behind your ear as far as you can.
2. Passive Flexibility : The ability to do movements with greater amplitude with external help is known as passive flexibility eg., stretching with the help of a partner, an accessory, or a prop.
Methods used to develop flexibility :
1. Slow Stretching: The first and the foremost way to improve flexibility is stretching the muscles around the joint slowly. The key point to note here is the stretching should be slow and without any jerky movements.
2. Ballistic Method: This form of stretching uses body’s momentum in an effort to extend range of motion. In this method, the movement is performed with a swing and in a rhythmic way. As the stretching is done in a rhythmic manner, it is called Ballistic Method.
Q6. What is coordinative abilities and explain different types of coordinative ability?
OR
Elucidate any 2 types of coordinative ability with suitable example.
Ans – Coordinative abilities are understood as relatively stabilised and generalised patterns of motor control and regulation processes. These enable the sportsman to do a group of movements with better quality and effect.
Types of coordinative ability –
1. Orientation Ability: Orientation ability is the ability to determine and change the position and movements of the body in required time and available space in relation to a definite field of action (such as a volleyball court, skating rink, or football ground) and/or a moving object (like a ball, opponent, or partner).
2. Coupling Ability: Coupling ability is the ability to coordinate body part movements with one another and in relation to a definite goal-oriented body movement. Coupling ability is important in sports like gymnastics and team games like football, basketball etc.
3. Rhythm Ability: Rhythm ability is the ability to perceive the rhythm of a movement and to perform the movement with the required rhythm. In some sports like gymnastics and figure skating the sportsperson has to perceive an external rhythm, music, and to express it in his movements.
4. Reaction Ability: This is the ability to react quickly and effectively to a stimulus. Different games and sports have different types of signals like visual, auditory and tactile to name a few. And to respond to such signals accurately and as quickly as possible is known as reaction ability.
5. Adaptation Ability: Adaptation ability is the ability to adjust or completely change the movement programme on the basis of changes and anticipated changes in the situation. These situational changes may be expected ones or may take place suddenly. It depends considerably on the speed and accuracy of perception of changes in the situation.