Most of students search over Google for Haryana Board (HBSE) Important Questions 2026. Here is the Main reason because HBSE Board Says that in HBSE Exam 2026 (last 3 Years of Questions will Repeat) so that here are the selected List of Questions of Haryana Board For Class 12.
HBSE Class 9 Math Important Question Answer 2026
Chapter 1 – Number System
Q1. The ![]() form of
form of ![]() is _______ .
is _______ .
Q2. Rationalise the denominator of ![]() .
.
Q3. Rationalize the denominator of ![]()
Q4. What will be get after rationalize the denominator of ![]() ?
?
Q5. The value of ![]() is
is
Q6. Find one rational number between 3 and 4.
Q7. Every rational number is an integer. (True/False)
Q8. Simplify: ![]()
Q9. Simplify : ![]()
Q10. Express 0.3333…….= ![]() in the form
in the form ![]() , where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0.
, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0.
Q11. Express 0.99999 _______ in the form ![]()
Q12. Express ![]() in the form
in the form ![]() , where p and q are integers and q≠ 0.
, where p and q are integers and q≠ 0.
Chapter 2 – Polynomials
Q1. Factorize the quadratic polynomial 6x2 + 5x – 6 .
Q2. Factorize : 27x3 + y3 + z3 – 9xyz Most Important
Q3. Factorise : 64m3 – 343m3
Q4. Factorise : ![]()
Q5. Factorise: 8a3 + b3 + 12a2b + 6ab2 Most Important
Q6. Evaluate 103 x 107 without direct multiplication.
Q7. Factorize: 4x2 + 9y2 + 16z2 + 12xy – 24yz – 16xz
Q8. Factorise : x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
Q9. Factorise: x3 – 2x2 – x + 2
Q10. Evaluate 103 x 107 by using identity.
Q11. Without actually calculating the cubes, find the value of (28)3 + (−15)3 + (−13)3.
Q12. Using suitable identity, find the value of (102)2.
Q13. Find the value of k for which x – 1 is a factor of the polynomial x2 + x + k .
Q14. Zero of p(x) = 3x + 1 is :
Q15. The coefficient of x2 in 2 – x2 +x3 is _________ .
Q16. The factors of 64m3 – 343n3 are __________.
Q17. What is product of ( x + 4 ) (x + 10) ?
Ans – x2 + 14x + 40
Q18. Write ![]() in expanded form.
in expanded form.
Q19. Find the value of k, if x = 2, y = 1 is a solution of the equation 2x + 3y = k
Q20. Find the value of k, if x – 1 is a factor of P(x), P(x) = 2x2 + kx + √2
Q21. Use the factor theorem factorize of x2 – 5x + 6 .
Q22. Factorize: 2x2 + 7x + 3
Q23. Factorize: 64x3 – 343y3
Q24. Factorize: 8x3 + y3 + 27z3 – 18xyz
Chapter 3 – Coordinate Geometry
Q1. In which quadrant or on which axis do each of the points (-2, 4), (3, -1), (-1, 0), (1, 2) lie? Verify your answer by locating them on the Cartesian plane.
Q2. Plot the following ordered pairs (x, y) of numbers as points in the Cartesian Plane:
| x | -2 | -3 | 3 | 0 |
| y | -3 | 7 | -1 | -1.5 |
Q3. Plot the following ordered pairs of numbers as points on the Cartesian Plane :
| x | 3 | -2 | -1 | 1 |
| y | -1 | 6 | -4 | -3 |
Q4. What is the name of each part of the plane formed by horizontal and the vertical lines in the Cartesian plane?
Q5. Point (5, -7) lies in which Quadrant ?
Q6. The point (0, 0) where x-axis and y-axis intersect is called _________ .
Q7. The abscissa and coordinate of (6, −4 ) is ________.
Q8. From the fig given below :
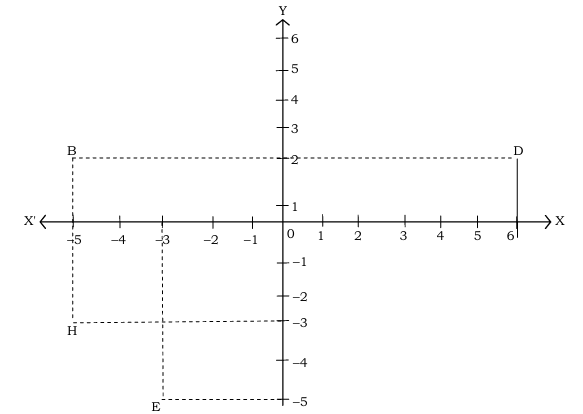
Write the answer of each of following from figure:
(i) The coordinates of B
(ii) The point identified by the coordinates (-3, -5)
(iii) The abscissa of the point D
(iv) The coordinate of point H
Q9.
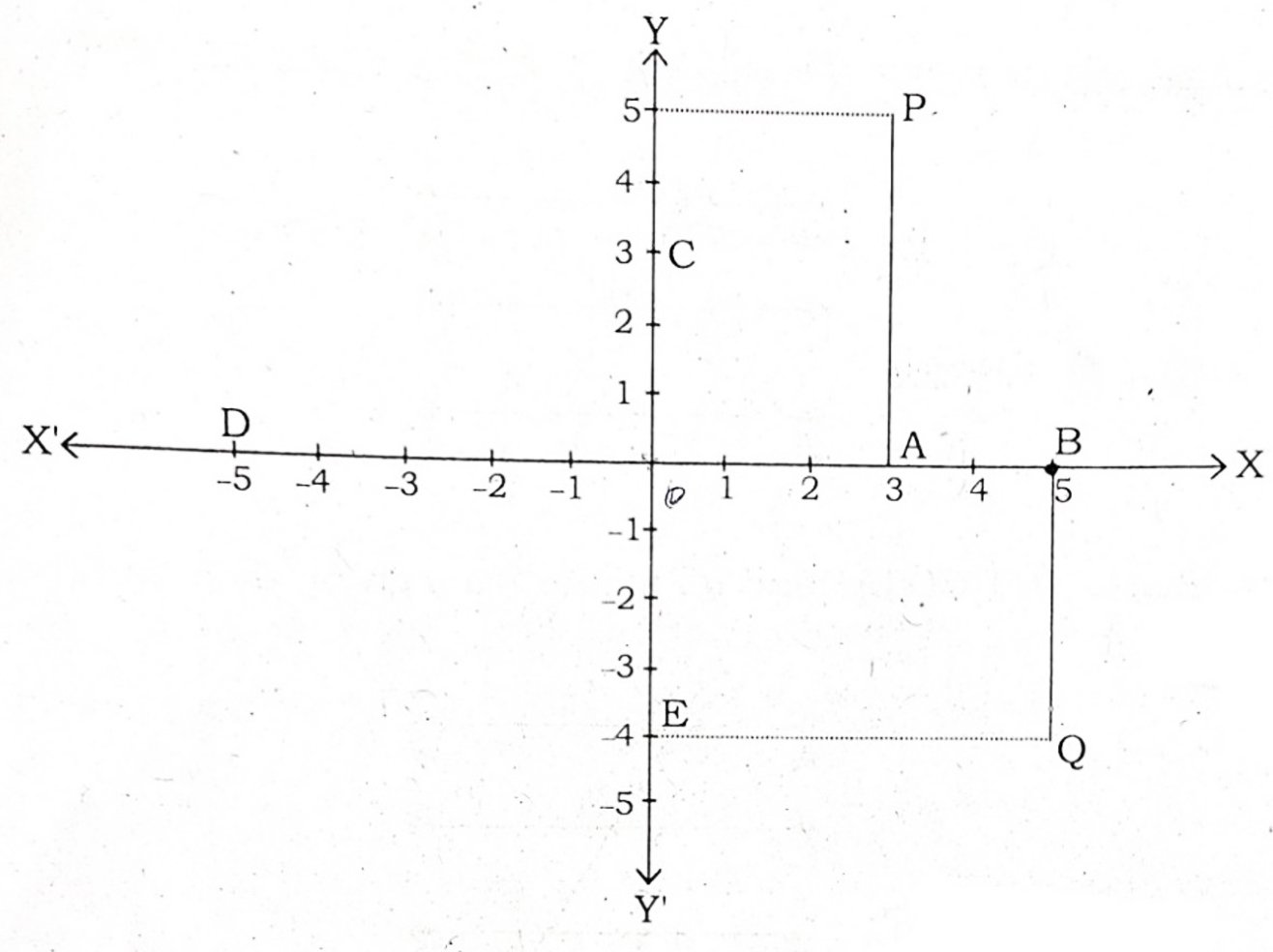
Look at the above figure and answer the following:
(i) Coordinates of A, B, C, D, E
(ii) Abscissa of point D
(iii) Ordinate of point E
(iv) Coordinates of point P, Q
Chapter 4 – Linear Equations in Two Variables
Q1. Find the four solutions for the equation 2x + y = 7 .
Q2. The floor of a rectangular hall has the perimeter 250 m. If the cost of the painting the four walls at the rate ₹ 12 per m2 is ₹ 18,000, find the height of the hall.
Q3. What is solution of (2x + 1) = x + 3
Q4. Solve the equation 2x + 1 = x – 3 and represent the solution on (i) The number line, (ii) The Cartesian plane.
Q5. Solve the equation 2x + 8 = 0 and represent the solution on (i) the number line (ii) the Cartesian plane.
Q6. Find four different solutions of the equation x+2y = 6.
Q7. Find the value of P if x = 2 , y = 1 is a solution of the equation 2x + 3y = P
Q8. The solution of a linear equation is not affected when the same number is added or subtracted from both the sides of the equation. (True/False)
Ans – True
Chapter 5 – Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry
Q1. What is second postulate of Euclid ?
Q2. Write the first postulate of Euclid.
Ans – A straight line may be drawn from any one point to any other point.
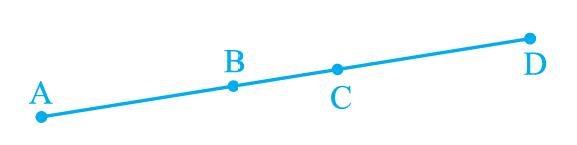
Q3. If in figure AC = BD, then prove that AB = CD : Most Important
Chapter 6 – Lines and Angles
Q1. Write the name of the point where these two lines intersect.
Q2. Give a definition for each of the following terms:
(i) Parallel lines.
(ii) Line segment
Q3. Define supplementary angle. Give its two examples also.
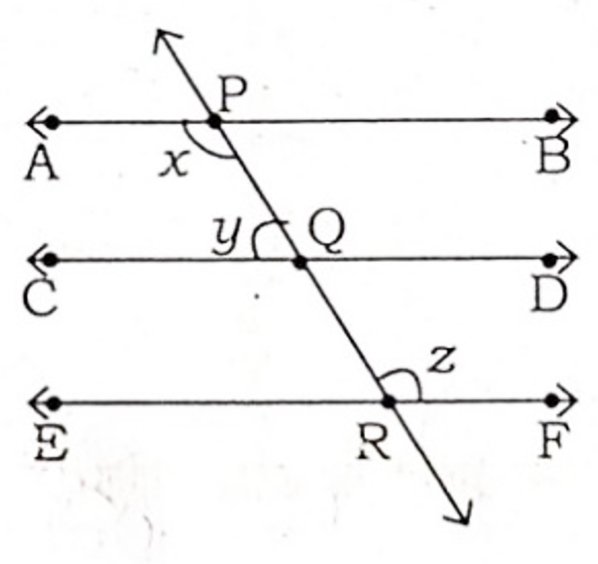
Q4. In the given figure, AB || CD || EF and y: z = 3 : 7 are given, then find the value of x.
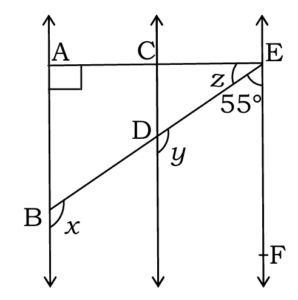
Q5. In fig., AB || CD and CD || EF. And EA ⊥ AB. If ∠BEF 55° then find the values of x, y and z.
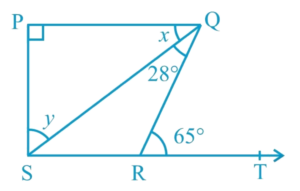
Q6. In fig., if PQ ⊥ PS, PQ || SR, ∠SQR = 28° and ∠QRT = 65°. Then find the values of x and y.
Q7. A terminated line can be produced indefinitely. (True / False )
Chapter 7 – Triangles
Q1. Prove that angles opposite to equal sides of an isosceles triangle are equal.
Q2. Show that the angles of an equilateral triangle are 60° each. Most Important
Q3. Construct a triangle ABC in which BC = 8cm, ∠B = 45° and AB – AC = 3.5 cm. Most Important
Q4. ABC is a triangle right angled at C. A line through the mid point M of hypotenuse AB and parallel to BC intersects AC at D. Show that:
(i) D is the mid point of AC
(ii) MDIAC
(iii) CM = MA = ![]() AB
AB
Q5. Construct a triangle ABC in which BC = 7 cm, ∠B – 75° and AB + AC = 13 cm. Most Important
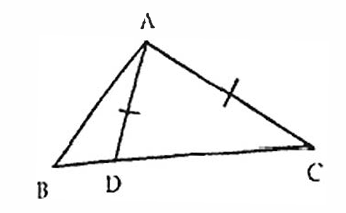
Q6. D is a point on side BC of ΔABC such that AD = AC in given figure show that AB > AD.
Q7. ΔABC is a right angled triangle in which ∠A = 90° and AB = AC. What is the value of ∠B and ∠C?
Q8. If ΔPRQ ≅ ΔCBA , then find:
(i) QR =…,.
(ii) PR =……
(iii) PO = …..
(iv) ∠B =…….
Q9. The triangle formed by joining the mid-points of the sides of an isosceles triangle is ________.
Q10. Construct a triangle ABC in which ∠B = 60°, ∠C = 45° and perimeter is 10 cm.
Q11. To construct a triangle we must know at least its ________ parts .
Q12. The sum of any two sides of a triangle is _______ than the third side.
Chapter 8 – Quadrilaterals
Q1. If the diagonals of a parallelogram are equal, then show that it is a rectangle.
Q2. Show that the diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular to each other. Most Important
Q3. ABCD is a quadrilateral in which P, Q, R and S are mid points of the sides AB, BC, CD and DA. AC is a diagonal, show that:
(i) SR || AC and SR=![]() AC
AC
(ii) PQ = SR
(iii) PORS is a parallelogram
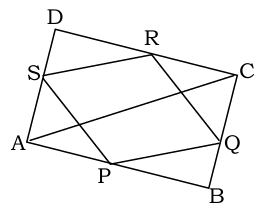
Q4. If two sides of a cyclic quadrilateral are parallel, prove that:
(i) remaining two sides are equal and
(ii) both diagonals are equal
Q5. Show that the line segments joining the mid-points of opposite sides of a quadrilateral bisect each other.
Q6. In cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, AOC is the diameter of circle. Ir ∠CAD = 50°, then ∠ACD is :
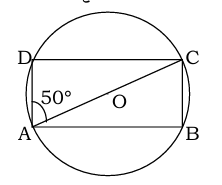
Q7. The diagonals of a rectangle are _______ .
Q8. If diagonal of a quadrilateral bisect each other, then quadrilateral is parallelogram. (True/False
Chapter 9 – Circles
Q1. Prove that a cyclic parallelogram is a rectangle.
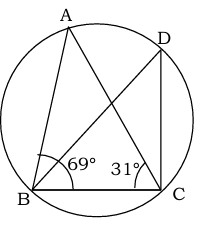
Q2. In figure angle ∠ABC = 69° and angle ∠ACB =31° find ∠BDC. Most important
Q3. A Roller 120 cm long has a diameter 84 cm. To level a playground, it takes 500 complete revolutions. Determine the area of playground in m2 .
Q4. Angles in the same segment of a circle are ______ .
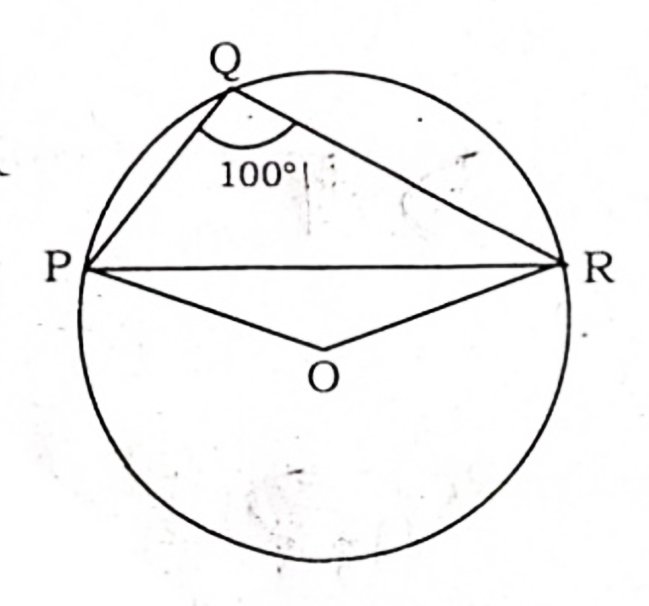
Q5. In the given figure ∠PQR = 100° , where P, Q and R are points on a circle with centre O. Find ∠OPR .
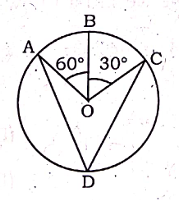
Q6. In fig., A, B and C are three points on a circle with centre O such that ∠BOC = 30° and ∠AOB = 60°. If D is a point on the circle other than the are ABC, then ∠ADC will be:
Q7. A circle has only finite numbers of equal chords. (True/False)
Ans – False
Chapter 10 – Heron’s Formula
Q1. Find the area of a triangle two sides of which are 18 cm and 10 cm and the perimeter is 42 cm.
Q2. Sides of a triangle are in the ratio of 3 : 5 : 7 and its perimeter is 300 cm. Find its area.
Chapter 11 – Surface Areas and Volumes
Q1. Find the volume of right circular cone with radius 6 cm and height 7 cm. Most Important
Q2. The height of a cone is 15 cm. If its volume is 1570 cm3. the radius of it base is ?
Q3. The volume of a right circular cone is 9856 cm3. If the diameter of the base is 28 cm. Find :
(i) Height of the cone
(ii) Slant height of the cone
(iii) Curved surface area of the cone
Q4. A conical tent is 10 m high and the radius of its base is 24 m. Find:
(i) Slant height of the tent.
(ii) Cost of the canvas required to make the tent, if the cost of 1 m2 canvas is ₹ 70.
Q5. The inner diameter of a circular well is 3.5 m. It is 10 m deep. Find:
(i) Its inner curved surface area.
(ii) The cost of plastering this curved surface at the rate of Rs. 40 per m2.
Q6. Volume of a hemisphere with radius r will be ________ .
Q7. Find the total surface area of a hemisphere if its radius is 21 cm
Q8. Find the radius of a sphere whose surface area is 154 cm2.
Chapter 12 – Statistics
Q1. The following table gives the lifetimes of 400 neon lamps :
| Lifetimes ( In Hours ) | Number of Lamps |
| 300-400
400-500 500-600 600-700 700-800 800-900 900-1000 |
14
56 60 86 74 62 48 |
(i) Represent the given information with the help of a histogram.
(ii) How many lamps have a lifetime of more than 700 hours?
Q2. The Blood Groups of 30 students of class IX are recorded as follows:
A, B, O, O, AB, O, A, O, B, A, O, B, A, O, O, A, AB, O, A, A, O, O, AB, B, A, O, B, A, B, O
Represent this data in the form of a frequency distribution table.
Q3. A family with a monthly income of 6,400 plans his budget for a month as given below :
| Grocery | Clothing | Education | Miscellaneous | Savings |
| 2100 | 600 | 1200 | 1500 | 1000 |
(i) Represent the above data by a bar-graph.
(ii) On which item they spent more?
Q4. Class mark of class 140-150 is _________.